|
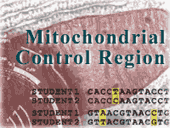 Mitochondrial
(mt) Point Mutations are single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) detected
in the ring-shaped chromosome found in the cell's energy-producing organelle.
Mutations are common in mt DNA, in large part due to exposure to oxygen
free radicals generated as a by-product of respiration. Mitochondrial
mutations can be used to retrace the common maternal lineage of modern
humans and to determine our relationship to the extinct hominid Neandertal. Mitochondrial
(mt) Point Mutations are single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) detected
in the ring-shaped chromosome found in the cell's energy-producing organelle.
Mutations are common in mt DNA, in large part due to exposure to oxygen
free radicals generated as a by-product of respiration. Mitochondrial
mutations can be used to retrace the common maternal lineage of modern
humans and to determine our relationship to the extinct hominid Neandertal.
|
|
 Alu
Insertion Polymorphism detects the presence or absence of a "jumping
gene" on chromosome 16. This simple genetic system has only two alleles
and three genotypes. Despite this simplicity, allele frequencies vary
greatly in different world populations. Alternate explanations about the
causes of this variation are consistent with opposing theories of the
origins of modern humans. Alu
Insertion Polymorphism detects the presence or absence of a "jumping
gene" on chromosome 16. This simple genetic system has only two alleles
and three genotypes. Despite this simplicity, allele frequencies vary
greatly in different world populations. Alternate explanations about the
causes of this variation are consistent with opposing theories of the
origins of modern humans. |



